Last Update:
Feb 19, 2026
Share
Companies with competitor-aligned pricing see 25-32% gains in new user acquisition compared to those with misaligned pricing strategies
Misaligned pricing increases CAC by 8-14% within the first quarter and reduces conversion rates by 15-20% on average
Quarterly pricing audits deliver 28% faster scaling compared to annual reviews, enabling rapid market response
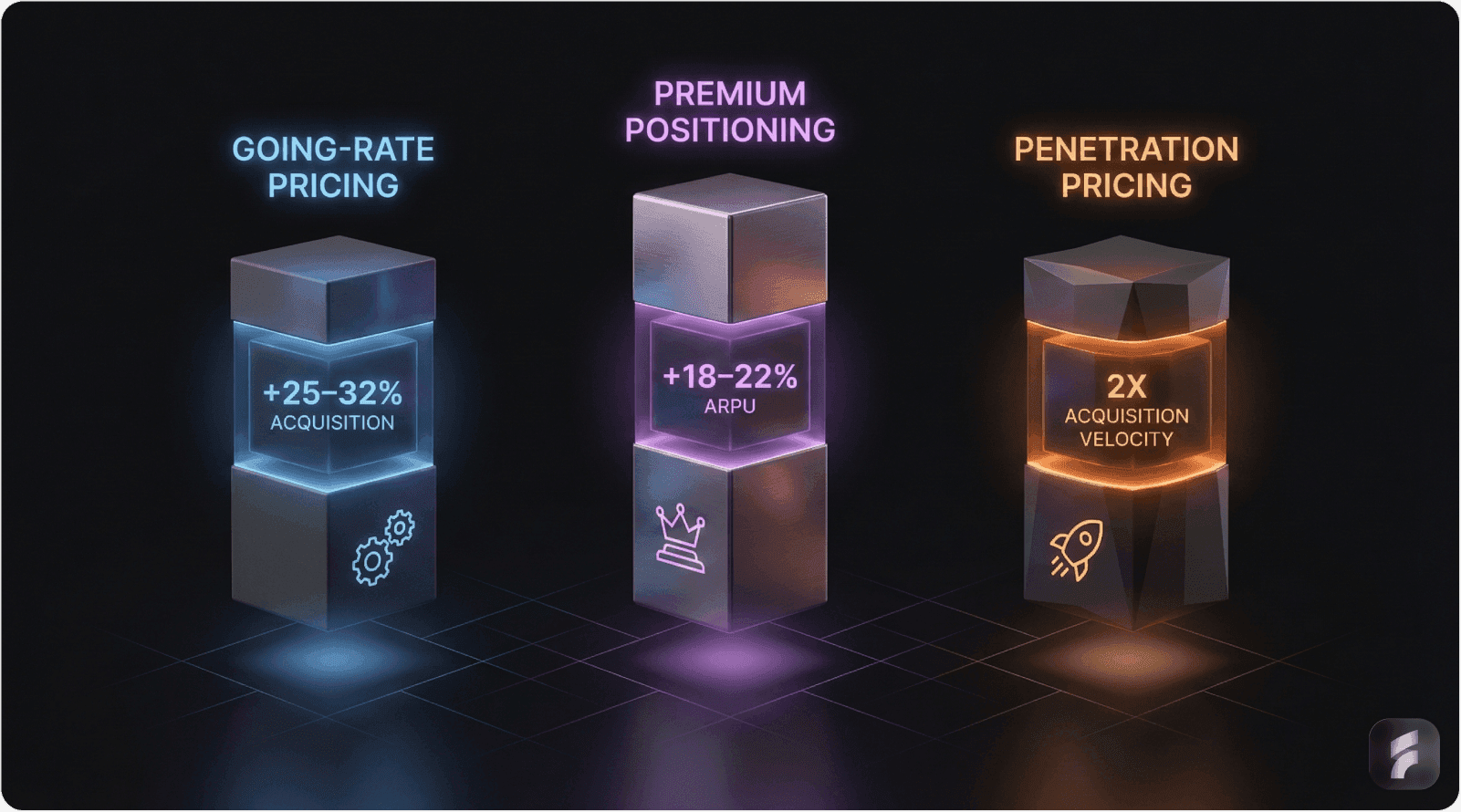
Three core pricing models (going-rate, premium, penetration) each offer distinct advantages when properly aligned with market dynamics
Real-time competitive intelligence reduces CAC by 17% during intense competitive periods through strategic micro-adjustments
Dynamic pricing capabilities enable companies to respond to market changes within days rather than months
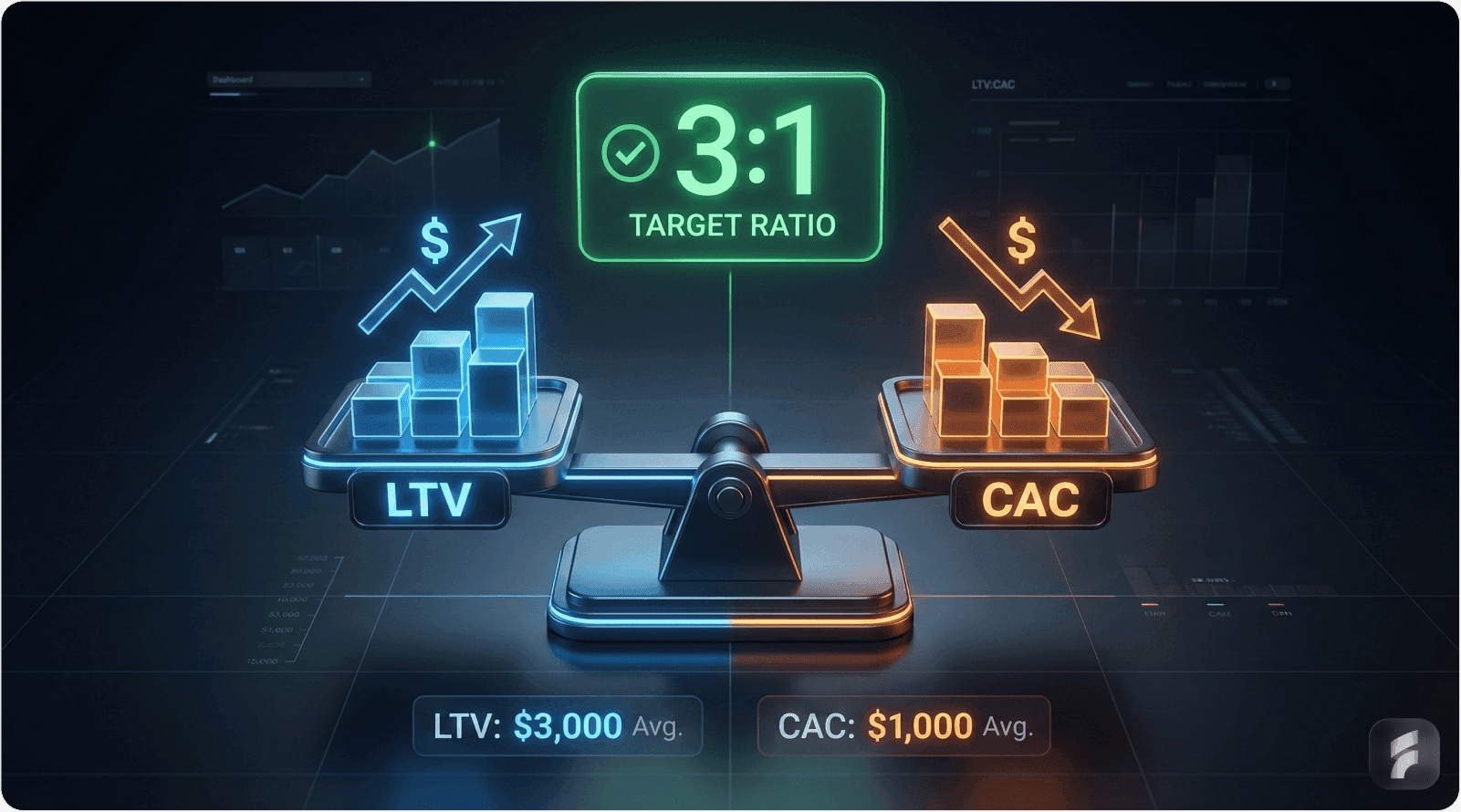
LTV:CAC ratio should be 3:1 or higher for sustainable SaaS growth and healthy unit economics
Introduction
Understanding how competitor pricing influences acquisition strategies has become essential for growth-focused companies. Research from Princeton University shows that optimized content visibility can increase by up to 40% when strategic techniques are properly applied. This comprehensive analysis explores the intricate relationship between competitive pricing dynamics and customer acquisition performance.
In today's hyper-competitive digital landscape, pricing decisions ripple through every stage of the customer journey. Companies that fail to monitor and respond to competitor pricing face acquisition cost increases of 8-14% on average, according to recent market analysis. For businesses focused on UX optimization and conversion improvement, pricing strategy represents a critical lever for growth.

Why Competitor Pricing Matters More Than Ever
The stakes have never been higher. Modern buyers conduct extensive research before making purchase decisions, with 87% of B2B customers considering price as a critical factor in their evaluation process.
This heightened price sensitivity means that even small misalignments with market rates can trigger significant consequences. When a company's pricing diverges from established market expectations, the entire acquisition funnel suffers—impacting everything from initial engagement to final conversion.
Definition: Market-Based Pricing
Market-Based Pricing is a strategic approach where companies set prices primarily by analyzing competitor rates, market positioning, and perceived value rather than solely relying on cost-plus calculations or internal metrics.
The Psychological Anchoring Effect
Competitor pricing creates powerful psychological anchors in customer minds. When prospects evaluate your offering, they unconsciously compare it against alternatives they've already researched.
This anchoring effect shapes perceived value before a single sales conversation begins. According to behavioral economics research from Stanford University, initial price exposure influences purchasing decisions for up to 60% of buyers, even when product features differ significantly.
Micro-Summary: Competitor pricing acts as a market signal that directly influences customer expectations, perceived value, and acquisition channel performance. Companies must understand these dynamics to optimize their go-to-market strategy effectively.
The Three Core Pricing Strategy Models
Market analysis reveals three distinct approaches companies use when positioning against competitors. Each model carries specific implications for acquisition velocity and customer lifetime value.
1. Going-Rate Pricing: The Market Match Strategy
Going-rate pricing involves setting prices at or near the market average established by key competitors. This approach minimizes price-based objections and allows companies to compete primarily on features, service quality, and brand reputation.
Companies using this model typically see 25-32% improvements in new user acquisition when properly aligned with market expectations. The strategy works particularly well for established players in mature markets where price wars have stabilized.
"Pricing alignment isn't about copying competitors blindly—it's about understanding market gravity and positioning strategically within it." — Pricing strategist research from McKinsey & Company
2. Premium Positioning: The Above-Market Approach
Premium pricing deliberately positions products 15-30% above competitive averages. This strategy signals superior quality, exclusive features, or enhanced service levels.
Data from SaaS benchmark studies shows that premium-positioned companies capture 18-22% higher average revenue per user (ARPU) but face longer sales cycles and more intensive qualification requirements. The approach succeeds when differentiation is genuine and communicable.
Companies pursuing premium strategies must invest heavily in demonstrating value. Marketing materials, case studies, and proof points become essential for justifying the price premium. Effective product design and UX audit processes help create the differentiated experience that justifies premium pricing.
3. Penetration Pricing: The Below-Market Strategy
Penetration pricing sets rates below competitive averages to rapidly acquire market share. This aggressive approach works best for new entrants or companies with strong retention mechanics that can monetize customers over time.
Research indicates that penetration pricing can accelerate acquisition velocity by 2x compared to market-rate competitors. However, the strategy requires careful financial planning to ensure unit economics remain viable.
Micro-Example: When Zoom entered the video conferencing market, their $14.99 monthly pricing significantly undercut established players. This penetration strategy helped them acquire over 300 million daily meeting participants within 18 months, despite fierce competition from well-funded incumbents.
Micro-Summary: The three core pricing models—going-rate, premium, and penetration—each offer distinct advantages for acquisition. Success requires aligning the chosen model with company capabilities, market dynamics, and long-term strategic objectives.
Quantifying the Pricing-Acquisition Connection
Hard data reveals the tangible impact of pricing decisions on acquisition performance. Companies that actively monitor and respond to competitor pricing movements consistently outperform those using static pricing models.
The Cost of Misalignment
When pricing diverges from market expectations, acquisition costs spike rapidly. Analysis of B2C technology companies shows that misaligned pricing increases customer acquisition cost (CAC) by 8-12% within the first quarter.
The impact compounds over time. If left uncorrected, pricing misalignment can reduce conversion rates by 15-20% while simultaneously increasing paid advertising costs due to lower engagement and higher bounce rates.
Key Statistics:
25-32% gains in new user acquisition for companies with competitor-aligned pricing
15-20% reduction in conversion rates with misaligned pricing on average
20-30% worse conversion for top-of-funnel traffic when pricing causes sticker shock
12-18% ARPU improvements from dynamic pricing adjustments
Geographic and Market Segment Variations
Pricing sensitivity varies significantly across geographic markets and customer segments. In Asia-Pacific markets, including rapidly growing hubs like Dhaka, pricing volatility in fintech sectors reached 22% between 2024-2026.
European markets show different dynamics due to regulatory frameworks. The Digital Markets Act (DMA) forced approximately 16% of SaaS companies to adjust pricing structures in 2025, creating opportunities for agile competitors.
Formula: Optimal LTV:CAC Ratio
The Acquisition Velocity Multiplier
Companies that benchmark competitor pricing quarterly demonstrate 28% faster scaling compared to those using annual pricing reviews. This velocity advantage compounds through network effects and market positioning.
In fintech specifically, companies adapting to 2025 competitive rate adjustments captured 20% more SMB signups despite industry-wide CAC increases of 14%.
Micro-Summary: Data consistently shows that pricing alignment directly correlates with acquisition performance. Companies monitoring competitive dynamics quarterly achieve measurably better growth trajectories than those with static pricing approaches.
Inside the Numbers: Comprehensive Performance Data
Performance Category | Metric | Aligned Strategy Gain | Misalignment Cost | Time to Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SaaS New Users | Acquisition Rate | +25-32% | -15-20% conversion | 1-3 months |
Fintech | CAC Cost Efficiency | -11% average | +8-14% spike | 2-4 weeks |
B2C | Churn Retention | -5-8% improvement | +12% cohort loss | 3-6 months |
Overall | ARPU Revenue Density | +18% lift | -10-15% decline | 2-5 months |
Market Share | Growth Velocity | 2x faster | Stagnant | 6-12 months |
This data, compiled from multiple industry sources including NetSuite market research and Gartner analysis, demonstrates consistent patterns across different business models and market segments.
Cohort Analysis Insights
Detailed cohort tracking reveals that pricing decisions impact different customer segments unequally. Enterprise customers show 40% less price sensitivity than SMB segments, allowing for more premium positioning in upper-market tiers.
However, SMB segments demonstrate higher acquisition velocity when pricing aligns within 5-10% of competitive averages. These customers typically conduct more limited research and make faster purchase decisions when price objections are minimal.
Micro-Summary: Performance data across SaaS, fintech, and B2C segments confirms that pricing alignment delivers measurable improvements in acquisition, retention, and revenue metrics within 1-6 month timeframes.
Expert Perspectives on Competitive Pricing
Industry leaders consistently emphasize the strategic importance of competitive pricing intelligence. Their insights reveal common patterns and successful approaches.
Strategic Intelligence as Foundation
"Competitor pricing is your market's gravity—ignore it, and acquisition orbits collapse."
This metaphor captures how pricing expectations shape the entire demand generation system. Sales teams armed with competitive pricing intelligence close deals 30% faster because they can address price objections proactively.
The Dynamic Response Imperative
"We track competitor pricing weekly because markets move faster than quarterly planning cycles," notes research from enterprise SaaS companies. This real-time monitoring approach enables rapid responses to competitive threats.
Static pricing models create vulnerability windows where competitors can capture market share through strategic adjustments. Companies using dynamic pricing frameworks maintain flexibility to respond within days rather than months.
"Real-time benchmarking reduced our CAC by 17% during intense competitive periods."
These gains came from micro-adjustments that kept pricing competitive without sacrificing margin excessively.
Integration Across Functions
Pricing strategy cannot live in isolation. Successful companies integrate competitive pricing intelligence across product, marketing, and sales functions.
"When our entire go-to-market team understands the competitive landscape, messaging becomes sharper and objection handling becomes natural," according to B2B SaaS research. This cross-functional alignment accelerates deal velocity and improves win rates.
Micro-Summary: Industry experts emphasize that competitive pricing intelligence must be real-time, cross-functional, and integrated into daily operations rather than treated as an annual strategic planning exercise.
Case Study Deep Dive: The UK Startup Pricing Crisis
This cautionary tale demonstrates how pricing misalignment can threaten even well-funded companies. A UK-based B2C technology startup with £10 million annual recurring revenue (ARR) faced near-catastrophic consequences from pricing decisions disconnected from competitive realities.
The Initial Success Formula
The company launched with lifetime subscription pricing at £99, creating strong viral acquisition loops. Word-of-mouth referrals drove 5,000 new customers monthly, with customer acquisition costs (CAC) hovering around £41 per customer.
The value proposition resonated clearly with early adopters. The lifetime pricing eliminated subscription friction and created a sense of exclusivity that powered referral mechanics.
By month 18, the company had acquired 50,000 users and attracted significant investor attention. Revenue growth and user metrics suggested a promising trajectory.
The Pressure to Pivot
Investor pressure for improved unit economics prompted a strategic pricing review in Q3 2023. Leadership decided to shift from lifetime pricing to annual subscriptions while simultaneously raising prices.
The new pricing structure launched at £199 annually—a 100% increase from the lifetime equivalent that early customers had paid. Critically, this decision proceeded without comprehensive competitive analysis.
Competitors were offering introductory annual tiers at £149 with free trial periods. The startup's new pricing positioned them 33% above market rates without commensurate differentiation.
The Acquisition Collapse
Within 60 days, acquisition velocity halved from 5,000 to 2,500 new customers monthly. Paid search campaigns that previously delivered steady growth suddenly became inefficient, with CAC rising 8% to £45.
More troubling patterns emerged in cohort analysis. New customers acquired at £199 pricing showed 22% faster churn rates compared to legacy lifetime customers. Average customer lifetime value (LTV) dropped from 9 months to just 3 months for new cohorts.
The company attempted A/B testing to validate the pricing, but they made a critical methodological error. They tested only on high-intent traffic sources, which masked the true market resistance to the new pricing.
Definition: Cohort-Based Analysis
Cohort-Based Analysis is a method of segmenting customers by acquisition date or characteristics to track how different groups behave over time, enabling precise measurement of how changes (like pricing adjustments) impact different customer segments.
Financial Impact Assessment
Six months after the pricing change, the financial picture had deteriorated significantly:
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR) growth stalled at 2% versus previous 15%
CAC payback period extended from 8 months to 16 months
The company had accumulated a £2 million backlog of loss-making customers
Investor confidence eroded, threatening the next funding round
Leadership finally commissioned comprehensive cohort dashboards that revealed the full extent of the pricing damage. The data showed clear causation between the pricing change and degraded unit economics.
The Recovery Strategy
In Q1 2025, the company implemented a complete pricing reset based on thorough competitive analysis:
Competitive Audit: Mapped all direct competitors' pricing tiers and promotional strategies
Market Positioning: Set new annual pricing at £129 to align with market averages
Promotional Layer: Added 20% discounts for annual prepayment
Monitoring System: Integrated competitor pricing alerts for ongoing tracking
Win-Back Campaign: Offered legacy customers attractive retention incentives
Results and Lessons
The recovery took three quarters to fully materialize, but results validated the new approach:
Year-over-year revenue growth recovered to +12%
Churn rates declined 9% as pricing aligned with value perception
Organic acquisition improved, reducing CAC by 15%
Annual recurring revenue stabilized at £12 million
"Cohort-by-acquisition-date analysis was our wake-up call. We were making strategic decisions on gut feel rather than competitive reality."
Micro-Summary: This case demonstrates how pricing decisions disconnected from competitive benchmarking can rapidly undermine acquisition and retention. Recovery requires comprehensive market analysis, pricing realignment, and rigorous cohort tracking to validate changes.
Case Study: Slack's Strategic Tier Wars Against Microsoft Teams
The competition between Slack and Microsoft Teams provides a masterclass in competitive pricing strategy within enterprise SaaS. This ongoing battle illustrates how market leaders respond to aggressive competitive threats.
The Competitive Landscape Shift
Before 2020, Slack dominated the team collaboration market with relatively stable pricing at $6.67 per user monthly for their Standard tier. Their product-led growth model and superior user experience drove consistent acquisition.
Microsoft's entry with Teams fundamentally disrupted the market. By bundling Teams with existing Office 365 subscriptions at effectively $0 incremental cost, Microsoft created intense pricing pressure.
Slack's Strategic Response
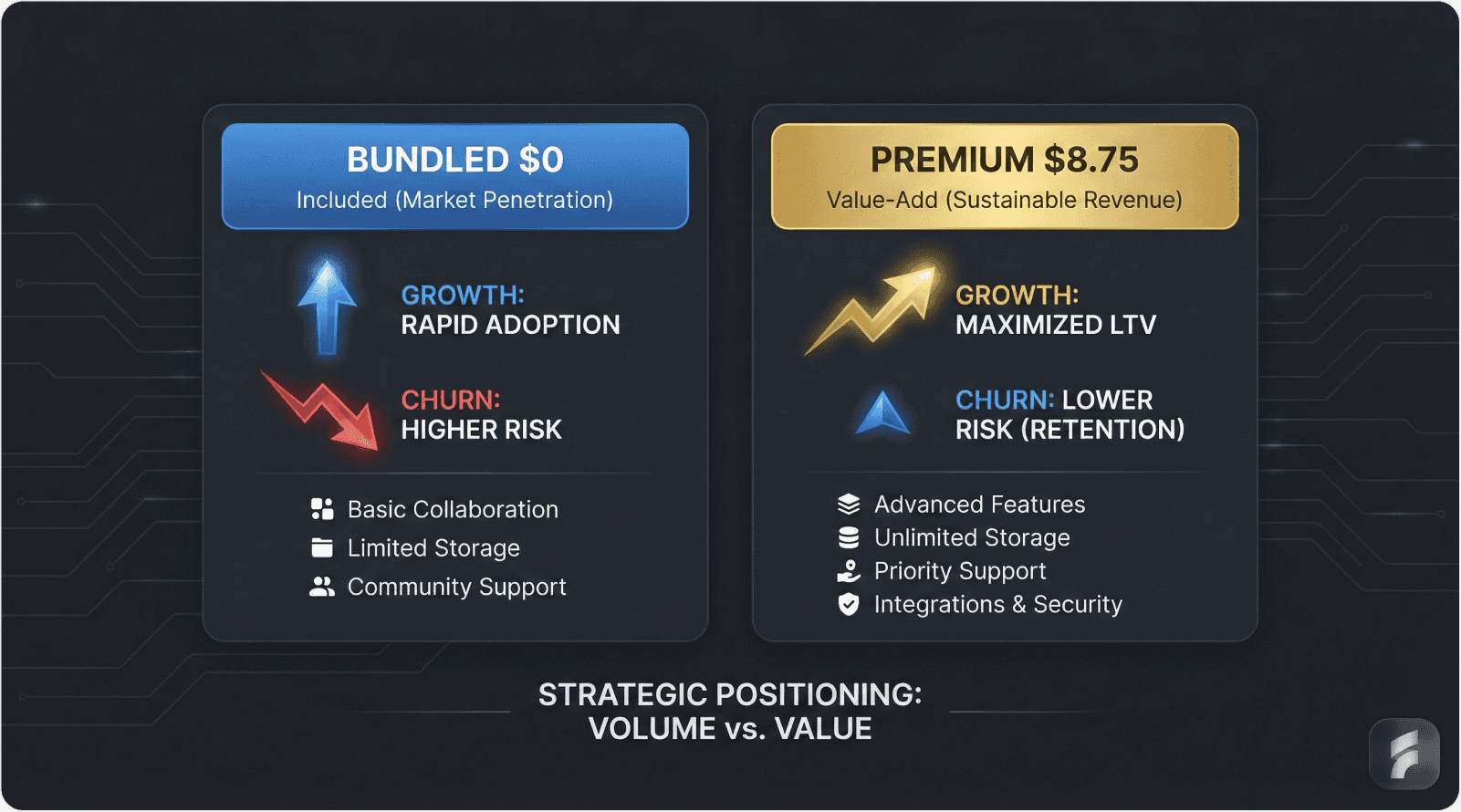
Rather than engaging in direct price competition, Slack expanded their freemium offering and introduced strategic tier adjustments:
Phase 1: Freemium Expansion (2020-2022)
Dramatically increased free tier capabilities
Introduced $8.75 Pro tier with enhanced features
Focused on user experience differentiation
Achieved 15,000 new team signups monthly
Phase 2: Feature Differentiation (2023-2024)
Launched AI-powered features at premium pricing
Created modular add-on structure
Maintained price positioning $3 above Microsoft equivalents
Emphasized superior integration ecosystem
Performance Outcomes
The strategy yielded measurable results:
User acquisition increased 28% year-over-year
However, churn on upgrading customers reached 11% as some users questioned value versus "free" Microsoft alternative
Product-led growth metrics showed strong top-of-funnel engagement
The 2025 Adjustment
Recognizing the churn challenge, Slack refined their approach in 2025:
Introduced AI add-ons priced competitively with enterprise alternatives
Enhanced value communication comparing total cost of ownership
Focused on switching costs and integration advantages
Improved onboarding to demonstrate differentiation quickly
Results from these adjustments:
32% user growth acceleration
ARPU increased 19% through successful upselling
Churn stabilized as value perception improved
"We price to win battles, not wars."
This philosophy reflects their focus on segment-specific competition rather than broad-market price wars.
Micro-Summary: Slack's response to Microsoft Teams demonstrates how premium-positioned companies can compete against lower-priced alternatives through strategic tier management, feature differentiation, and value-based messaging rather than direct price matching.
Case Study: Stripe vs PayPal—Fintech Pricing Competition
The payments processing market provides clear examples of how pricing strategy directly impacts acquisition in transactional businesses. The ongoing competition between Stripe and PayPal illustrates dynamic pricing in action.
Market Context and Positioning
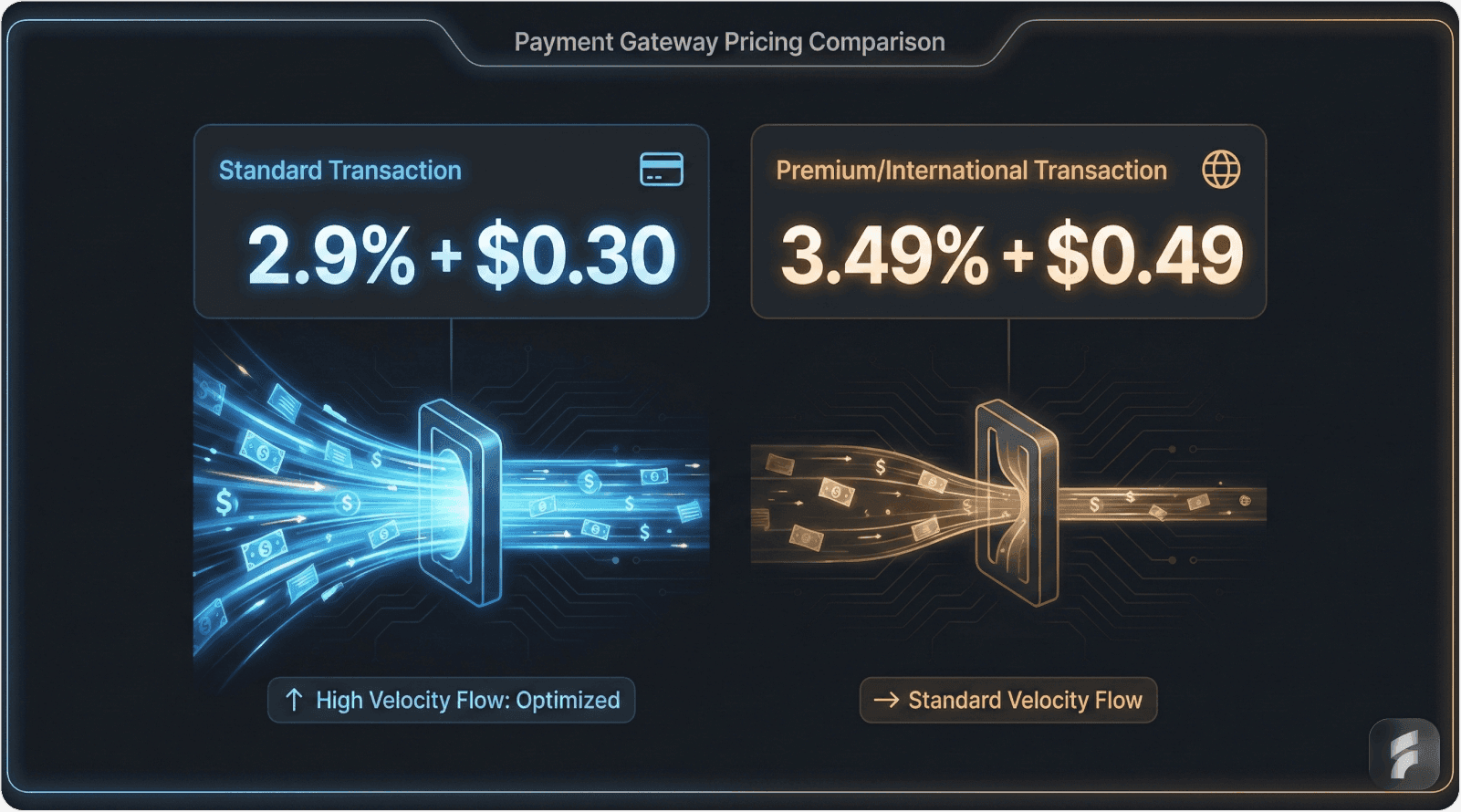
PayPal entered 2024 with established small business pricing at 3.49% + $0.49 per transaction. Their brand recognition and consumer trust provided strong advantages, but their pricing left room for competitor disruption.
Stripe recognized the opportunity and launched aggressive SMB-focused pricing in 2025 at 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction—a 17% reduction in effective rate for typical transactions.
Strategic Pricing Architecture
Stripe's approach went beyond simple price reduction:
Volume-Based Tiers: Automatic discounts as transaction volume increased
Modular Product Suite: Billing, invoicing, and subscription tools priced separately
Transparent Pricing: Clear, published rates versus negotiated enterprise contracts
Developer-Friendly: Simple API integration reducing switching costs
This modular architecture allowed customers to start with basic payment processing and expand into adjacent services, increasing both retention and revenue per customer.
Acquisition Impact
The pricing adjustment triggered significant market movement:
25% surge in SMB signups within first six months
CAC decreased 14% through referral-driven growth
Payment volume reached $1.4 trillion in 2025, up 22% year-over-year
Market share in SMB segment increased 8 percentage points
PayPal's Counter-Strategy
PayPal responded with their own pricing adjustments:
Introduced 0% transaction fees for first 90 days
Enhanced buyer protection messaging to justify rates
Launched working capital products at competitive rates
Emphasized ecosystem advantages and consumer reach
The competitive dynamic benefited customers but compressed margins across the industry. Both companies invested heavily in value-added services to justify their pricing.
Lessons for Payment Processors
This competition reveals several principles:
Transparency Wins: Published pricing reduces sales friction in SMB segment
Modular Pricing: Allows customers to expand usage without forced bundling
Speed to Market: Quick pricing adjustments capture market momentum
Volume Economics: Transaction-based pricing must account for economies of scale
"Granular rival tracking shortened our sales cycles by 25%."
Real-time pricing awareness enabled sales teams to position proactively.
Micro-Summary: The Stripe-PayPal pricing competition demonstrates how aggressive pricing moves combined with product innovation can rapidly shift market share in transaction-based businesses where switching costs are relatively low.
SaaS-Specific Considerations: Onboarding and Tier Design
For SaaS companies, pricing strategy extends beyond simple rate setting. The entire user experience must communicate and justify pricing decisions from first contact through renewal.
Onboarding Flow Integration
Modern SaaS onboarding increasingly incorporates competitive positioning. Companies like Intercom benchmark against competitors such as Zendesk (priced $19-115 per user) when designing their onboarding sequences.
By launching a $39 Starter tier with clear feature comparisons and AI upsell pathways, Intercom improved trial-to-paid conversion by 27%. The onboarding experience explicitly addressed competitive alternatives.
Key Onboarding Principles:
Immediate Value Delivery: Show core value before discussing pricing
Transparent Tier Comparisons: Help users self-select appropriate tier
Competitive Context: Acknowledge alternatives and explain differentiation
Friction Reduction: Remove unnecessary steps between trial and payment
Dashboard-Based Pricing Visibility
Product dashboards increasingly surface pricing and upgrade prompts contextually. Rather than generic "upgrade now" messages, successful SaaS products tie pricing discussions to specific usage patterns and needs.
When users approach feature limits or usage thresholds, contextual messaging can reduce objections by 18% by framing upgrades as natural progressions rather than sales pitches.
HR SaaS Market Examples
The HR technology market demonstrates tier strategy effectively. BambooHR positioned at $6-8 per user monthly versus Workday's $100+ enterprise pricing created clear market segmentation.
BambooHR's penetration pricing acquired 40% of the SMB market within three years. As these customers grew, many upgraded to mid-market tiers, creating a natural expansion revenue stream.
This "land and expand" strategy works particularly well when:
Product usage scales naturally with company growth
Feature needs evolve as organizations mature
Switching costs increase over time through data accumulation
Integration ecosystem creates lock-in effects
At Saasfactor, we help companies optimize their entire user journey—from onboarding through retention—to maximize the effectiveness of pricing strategies.
Micro-Summary: SaaS companies must integrate pricing strategy into product experience through thoughtful onboarding, contextual upgrade prompts, and tier designs that support natural customer progression.
Fintech-Specific Dynamics Across Payment, Lending, and PropTech
Financial technology markets demonstrate unique pricing characteristics due to regulatory constraints, transaction economics, and trust requirements.
Payment Processing Competition
The payment processing market operates on razor-thin margins with intense competition. Square's 2.6% + $0 flat rate versus Stripe's 2.9% + $0.30 creates meaningful differentiation for specific transaction profiles.
For average transaction sizes below $20, Square's structure becomes more attractive. Above $40, Stripe's percentage-based model often wins. Sophisticated merchants calculate their specific economics before choosing providers.
This has driven providers toward more sophisticated pricing:
Industry-specific rates for restaurants, retail, professional services
Volume-based tiering that rewards scale
Bundled pricing that includes POS hardware and software
International transaction rates as differentiators
The pricing competition forced 2026 industry adjustments that ultimately benefited merchants through 16% lower effective rates across the market.
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Dynamics
The BNPL market between Affirm, Klarna, Afterpay and others demonstrates consumer-facing pricing strategy. By offering 0% APR options funded through merchant fees, these platforms removed consumer price sensitivity.
This shifted competition to:
Merchant acquisition based on conversion lift promises
Consumer experience and approval rates
Retailer partnership exclusivity
Brand trust and financial stability
0% consumer pricing drove 30% faster acquisition compared to traditional installment lending. The strategy works because merchants subsidize costs in exchange for higher conversion rates and larger average order values.
Property Technology Innovation
PropTech platforms like Zillow demonstrate freemium models in transaction-heavy markets. By offering free property search to consumers while charging real estate agents for leads and enhanced listings, Zillow reduced CAC by 20% compared to paid advertising models.
Their pricing strategy creates a two-sided marketplace where:
Consumers receive free value that drives engagement
Real estate professionals pay for access to engaged consumers
Transaction facilitation services generate additional revenue
Data monetization through mortgage and insurance products
This approach contrasts with Realtor.com's premium consumer subscription model, creating clear market segmentation.
Micro-Summary: Fintech pricing strategies must account for transaction economics, regulatory requirements, multi-sided marketplace dynamics, and trust building. Successful players often use free or low-cost consumer pricing subsidized by business customer revenue.
Emerging Dynamics in AI and Multi-Agent SaaS
The rapid evolution of AI-powered SaaS introduces new pricing considerations and competitive dynamics. Early market formation means pricing strategies will significantly influence market structure.
AI Agent Pricing Models
Companies like Adept and Anthropic are establishing pricing precedents for AI agent services. Current models range from $20-50 monthly for individual users to enterprise licensing based on usage volume.
Key pricing questions remain unsettled:
Per-agent versus per-user pricing structures
Usage-based versus flat subscription models
Orchestration and multi-agent premium pricing
API access versus interface-based pricing
Early movers like ElevenLabs in voice AI deliberately undercut anticipated market prices at $5 monthly, achieving 3x user growth within six months. This penetration strategy aims to establish market leadership before competition intensifies.
Voice UX and Conversational Interfaces
Voice-enabled interfaces introduce pricing complexity around usage patterns. Unlimited voice minutes versus per-minute pricing creates different user behaviors and acquisition characteristics.
Companies testing voice pricing discovered that:
Flat-rate "unlimited" pricing increased trial conversion by 35%
Per-minute pricing attracted lower-volume, price-conscious users
Hybrid models with generous free tiers optimized for growth
Enterprise contracts typically used seat-based pricing regardless of usage
Platform Orchestration Premiums
Multi-agent AI platforms that orchestrate various AI capabilities can command 15% premiums over single-purpose tools. This reflects the integration value and reduced complexity for customers managing multiple AI solutions.
However, this premium requires clear demonstration of:
Actual integration time savings
Performance improvements from orchestration
Simplified management and monitoring
Consolidated billing and support
Micro-Summary: AI-powered SaaS markets are in price discovery phase, with strategies ranging from penetration pricing to premium orchestration models. Early pricing decisions will influence market structure as the category matures.
Implementation Framework: The 7-Step Competitive Pricing Audit
Systematic competitive analysis requires structured methodology. This seven-step framework enables quarterly pricing reviews that maintain market alignment.
Step 1: Competitor Identification and Segmentation
Begin by mapping 10-15 competitors across direct and indirect categories:
Direct Competitors: Offer similar solutions to identical target markets
Indirect Competitors: Solve the same problem through different approaches
Aspirational Competitors: Where you aim to position in 12-24 months
Disruptive Threats: Emerging players with novel approaches
Tools like Contify, SimilarWeb, and category-specific databases help identify comprehensive competitor sets.
Step 2: Pricing Intelligence Gathering
Systematically collect pricing data across competitor sets:
Published pricing from websites and pricing pages
Promotional offers and discount structures
Bundle configurations and upsell pathways
Enterprise vs SMB pricing variations
Geographic and market segment differences
Create pricing matrices comparing features and tiers across competitors. Many companies use competitive intelligence platforms or manual spreadsheet tracking.
Step 3: Segmentation Analysis
Organize collected data by customer segment:
SMB Segment: Annual contract value $0-10,000
Mid-Market: Annual contract value $10,000-100,000
Enterprise: Annual contract value $100,000+
Pricing sensitivity varies dramatically across segments. SMB customers show 40% higher price sensitivity than enterprise buyers, requiring different positioning strategies.
Step 4: Willingness-to-Pay Assessment
Survey existing customers and prospects to measure price sensitivity:
Van Westendorp Price Sensitivity Meter
Conjoint analysis for feature-price tradeoffs
A/B testing of pricing page variations
Sales conversation analysis for objection patterns
Target 87% alignment between your pricing and customer willingness-to-pay thresholds to optimize conversion while maximizing revenue.
Formula: Customer Lifetime Value Calculation
Step 5: LTV Impact Modeling
Project how pricing changes affect customer lifetime value:
Revenue impact from price changes
Churn rate sensitivity to pricing
Upgrade and expansion revenue effects
Competitive win rate implications
Build scenario models comparing current pricing against 3-5 alternatives. Include best case, likely case, and worst case assumptions for each scenario.
Step 6: A/B Testing Implementation
Test pricing variations with live traffic:
Dedicate sufficient sample size for statistical significance
Run tests minimum 4-6 weeks to account for buying cycle variation
Segment results by customer characteristics and traffic sources
Measure conversion, revenue, and leading indicators of retention
Common testing approaches include:
Price point variations (e.g., $49 vs $59)
Tier structure changes (number and spacing of tiers)
Promotional offer effectiveness
Bundling and unbundling strategies
Step 7: Go-to-Market Integration
Operationalize competitive pricing intelligence across teams:
Sales Enablement: Create battlecards showing competitive positioning
Marketing Materials: Develop comparison pages addressing alternatives
Product Roadmap: Prioritize features that justify premium positioning
Customer Success: Train on value realization that reduces churn
Expected outcomes from complete framework implementation:
15-25% reduction in customer acquisition cost
Improved win rates in competitive sales situations
Faster sales cycles through proactive objection handling
Higher revenue per customer through optimal pricing
Micro-Summary: Systematic competitive pricing audits enable data-driven pricing decisions. The seven-step framework provides structure for quarterly reviews that maintain market alignment while optimizing unit economics.
Building Dynamic Pricing Capabilities
Static annual pricing reviews cannot match the pace of modern markets. Companies increasingly invest in dynamic pricing capabilities that enable rapid responses to competitive movements.
Technology Infrastructure Requirements
Dynamic pricing requires integrated systems:
Competitive Intelligence Feeds: Automated monitoring of competitor pricing changes
Customer Analytics: Real-time tracking of conversion, retention, and expansion metrics
Financial Modeling: Automated scenario analysis for proposed changes
A/B Testing Platform: Systematic experimentation infrastructure
CRM Integration: Connecting pricing decisions to sales and success workflows
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Configure alerts for significant competitive pricing changes:
New competitor tier introductions
Promotional campaigns from key rivals
Significant price increases or decreases
Feature additions that affect comparative value
Market-wide pricing trends
Leading companies check competitor pricing weekly or configure automated daily scans. This enables responses within days rather than quarters.
Cohort-Based Performance Tracking
Monitor pricing impact by acquisition cohort:
Group customers by acquisition date
Track CAC, LTV, churn, and expansion revenue by cohort
Compare cohorts before and after pricing changes
Measure time-to-value and product adoption patterns
This granular analysis reveals true pricing impact separated from other market variables.
Micro-Summary: Dynamic pricing capabilities require technology infrastructure, real-time monitoring, clear decision frameworks, and cohort-based analytics. Companies investing in these systems respond faster to market changes and optimize pricing continuously.
Common Pitfalls and Counterstrategies
Even sophisticated companies make predictable pricing mistakes. Understanding these pitfalls enables proactive avoidance.
Pitfall 1: Margin Erosion Through Blind Matching
Simply matching competitor prices without considering your cost structure and value proposition erodes margins unnecessarily. Companies that blindly match competitors often see profit margins decline 12% while acquisition gains remain modest.
Counter-Strategy: Implement value-based pricing overlays that justify premium positioning. Zoom's $15 monthly tier with premium features like cloud recording and longer meeting durations commands pricing power through clear differentiation.
Document and communicate:
Unique features unavailable in competitive alternatives
Superior service levels or support quality
Integration advantages or ecosystem benefits
Total cost of ownership advantages
Pitfall 2: Regulatory Compliance Risks
The European Digital Markets Act forced approximately 10% of SaaS companies to adjust pricing in 2025, creating unexpected CAC increases. Companies operating globally face complex regulatory landscapes affecting pricing flexibility.
Counter-Strategy: Build scenario models for regulatory changes:
Monitor proposed regulations in key markets
Model pricing adjustments required for compliance
Assess impact on acquisition economics
Develop communication strategies for price changes
Maintain pricing flexibility through tier structure design that accommodates regional variations without fragmenting the product experience.
Pitfall 3: Organizational Data Silos
Research indicates 40% of companies lack integrated systems connecting competitive intelligence, customer analytics, and financial planning. This fragmentation slows decision-making and reduces pricing agility.
Counter-Strategy: Invest in platforms like Arensic, Klue, or Crayon that centralize competitive intelligence. Ensure these systems integrate with:
CRM systems for sales enablement
Business intelligence tools for financial modeling
Marketing automation for campaign coordination
Product analytics for feature usage tracking
Pitfall 4: Insufficient Testing Before Launches
The UK startup case study illustrated how inadequate testing—particularly testing only high-intent traffic—masked true market resistance to pricing changes.
Counter-Strategy: Design testing protocols that include:
Diverse traffic sources (organic, paid, referral, direct)
Multiple customer segments and personas
Sufficient sample sizes for statistical confidence
Extended time periods capturing buying cycle variation
Leading and lagging indicator measurement
Never launch major pricing changes without rigorous validation across representative customer populations.
Pitfall 5: Promotional Addiction
Companies sometimes become dependent on promotional discounting to maintain acquisition velocity. This trains customers to wait for deals and erodes perceived value.
Counter-Strategy: Use promotions strategically and sparingly:
Time-bound promotions for specific market events
New customer acquisition only (not broadly advertised)
First-purchase discounts with full-price renewals
Value-add bonuses instead of percentage discounts
The UK startup found that "promotional campaigns failed without benchmarking—organic channel revival ultimately stabilized us," according to post-recovery analysis.
Micro-Summary: Common pricing pitfalls include margin erosion, regulatory risks, data silos, insufficient testing, and promotional addiction. Each has proven counter-strategies that sophisticated pricing teams implement proactively.
Longitudinal Market Analysis: Pricing Trends 2020-2026
Understanding multi-year pricing trends reveals cyclical patterns and emerging dynamics that inform strategy.
The COVID Era: Aggressive Penetration (2020-2022)
The pandemic accelerated digital adoption, triggering aggressive penetration pricing across SaaS and fintech. Companies prioritized land grab over unit economics, resulting in:
35% increase in new customer acquisition across categories
CAC increases of 22% as competition intensified
Dramatic expansion of freemium offerings
Widespread promotional campaigns and extended trials
This period established new baseline expectations that persisted after markets normalized.
Market Stabilization Phase (2023-2024)
As pandemic urgency faded, markets began rationalizing:
Pricing gradually increased as growth-at-all-costs moderated
Unit economics received renewed focus from investors
M&A activity consolidated fragmented categories
Dynamic pricing adoption increased 28%
Companies that had acquired customers unprofitably faced difficult retention challenges as they attempted price increases on existing cohorts.
The AI Disruption Era (2025-2026)
Generative AI capabilities triggered new competitive dynamics:
AI-enhanced products justified 15-25% premium pricing
Traditional products faced pressure to match capabilities
New AI-native entrants challenged incumbents
Usage-based pricing gained traction for AI features
Market forecasts suggest that by 2027, 65% of B2B SaaS will incorporate some usage-based pricing component, particularly for AI-powered features.
Performance Patterns Across Eras
Companies actively benchmarking competitors outperformed static pricers by 2.1x in ARR growth across all periods. This consistent advantage stems from:
Faster response to market shifts
Better alignment with customer expectations
Reduced vulnerability to competitive disruption
More effective value communication
In fintech specifically, post-2024 political changes hinted at potential tariff volatility affecting international pricing, though direct impacts remained limited through 2026.
Micro-Summary: Six-year pricing trend analysis reveals that companies with dynamic pricing capabilities consistently outperformed static competitors across market cycles. Current trends toward AI integration and usage-based models will likely accelerate in coming years.
Product Spotlight: Winning Tactics From Market Leaders
Examining specific company approaches reveals patterns that drive acquisition success.
Zoom: Usage Caps as Differentiation
Zoom's $14.99 tier versus Microsoft Teams' $0 bundled offering demonstrates strategic positioning through usage limitations:
Free tier limited to 40-minute meetings for 3+ participants
Paid tier removed time restrictions while adding features
Created natural upgrade path as teams scaled usage
Generated 300% acquisition growth during peak demand
The strategy worked because the free tier provided genuine value for small teams while the upgrade value proposition was clear and immediate for growing organizations.
Notion: Freemium Disruption of Established Players
Notion's approach to competing with Evernote illustrated effective freemium positioning:
Generous free tier with meaningful capabilities
Clear feature gating that aligned with team growth
Collaborative features that drove viral adoption
45% user growth within 18 months of launch
By making the core product experience available for free, Notion reduced acquisition friction while building habits that led to eventual conversion.
HubSpot: Free CRM Strategy
HubSpot's decision to offer completely free CRM while Salesforce charged $25+ per user monthly exemplified aggressive land-grab strategy:
Acquired 1 million+ users within 24 months
Created upgrade paths to marketing and sales automation
Established data lock-in through accumulated contact history
Generated expansion revenue from 30% of free users
The strategy succeeded because the free CRM created genuine value while introducing users to the HubSpot ecosystem, setting up natural expansion opportunities.
Figma: Collaborative Pricing Model
Figma's approach to competing with Adobe XD and Sketch demonstrated innovative thinking:
Free tier for up to 3 projects
Collaboration features available across all tiers
Pricing based on editor seats but unlimited viewers
Viral growth through designer-to-designer sharing
This pricing structure aligned with actual collaborative workflows, making Figma the natural choice for design teams versus traditional individual-seat licensing models.
Micro-Summary: Market leaders demonstrate that successful pricing strategies often involve generous free tiers, clear upgrade paths, alignment with natural usage patterns, and viral adoption mechanics rather than simply undercutting competitor prices.
Synthesis: Building Sustainable Acquisition Advantage
Mastering the competitive pricing and acquisition nexus requires integrating multiple capabilities across strategy, operations, and culture.
Strategic Integration Requirements
Successful companies treat pricing as a cross-functional discipline:
Product Teams: Design features and tiers that support pricing strategy
Marketing Teams: Communicate value and position against alternatives
Sales Teams: Leverage competitive intelligence in deal progression
Finance Teams: Model economics and maintain healthy unit economics
Customer Success: Drive retention and expansion revenue realization
This integration ensures pricing decisions consider all stakeholder perspectives and cascade effectively through operations.
Data-Driven Decision Culture
Organizations that excel at competitive pricing share cultural characteristics:
Default to testing rather than opinions
Make decisions based on cohort data analysis
Respond rapidly to market signals
Maintain customer-centric value focus
Balance growth and profitability objectives
Leadership must champion this data orientation and provide teams with tools, training, and authority to act on insights.
Continuous Learning Systems
Market dynamics evolve continuously. Build organizational capabilities for ongoing learning:
Regular competitive tear-downs and analysis sessions
Post-mortem reviews of won and lost deals
Customer advisory boards providing feedback
Industry benchmark participation
Cross-functional pricing councils
The Path Forward
The companies profiled throughout this analysis—Stripe's modular precision, Slack's agile positioning, HubSpot's freemium vision, and others—share common threads:
Market Awareness: Deep understanding of competitive dynamics
Customer Insight: Regular validation of value perceptions
Operational Agility: Ability to adjust quickly when needed
Value Discipline: Focus on demonstrable customer outcomes
As AI capabilities, regulatory requirements, and market structures continue evolving, these foundational capabilities will become even more critical.
Companies that build systematic competitive pricing intelligence today will compound advantages over time through better acquisition efficiency, stronger retention, and more effective revenue expansion.
Our team at Saasfactor specializes in helping companies build these capabilities through comprehensive UX optimization, strategic product design, and data-driven UX audits that align pricing strategy with user experience.
Micro-Summary: Sustainable acquisition advantage through pricing requires strategic integration across functions, data-driven culture, continuous learning systems, and operational capabilities that enable rapid market response.
Glossary of Key Terms
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Total sales and marketing expenses divided by number of new customers acquired in a period. Critical metric for assessing acquisition efficiency and unit economics.
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): Predicted total revenue a customer will generate over their entire relationship with a company. Calculated as (ARPU × Gross Margin) / Churn Rate. Used to determine appropriate acquisition investment levels.
Churn Rate: Percentage of customers who stop using a product or cancel subscriptions within a given timeframe. Calculated as (customers lost / total customers at start) × 100. Critical retention metric affecting LTV and growth.
Average Revenue Per User (ARPU): Total revenue divided by number of users or accounts. Measures monetization efficiency and helps track impact of pricing changes and upselling success. Also called Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA) in B2B contexts.
Penetration Pricing: Strategy of setting prices below market averages to rapidly acquire customers and gain market share. Often used by new entrants or companies with cost advantages. Requires careful unit economics management.
Premium Positioning: Pricing strategy that sets prices 15-30% above market averages to signal superior quality, features, or service. Requires strong differentiation and value communication. Successful when targeting less price-sensitive segments.
Going-Rate Pricing: Setting prices at or near market averages established by key competitors. Minimizes price-based objections and allows competition on features and service. Most common in mature markets.
Market-Based Pricing: Pricing strategy primarily determined by competitor rates and market positioning rather than cost-plus calculations. Requires regular competitive intelligence gathering to maintain appropriate positioning.
Cohort Analysis: Method of grouping customers by common characteristics (typically acquisition date) to track performance over time. Enables measurement of how changes like pricing adjustments impact different segments. Essential for validating decisions.
LTV:CAC Ratio: Customer lifetime value divided by customer acquisition cost. Measures relationship between customer value and acquisition investment. Healthy B2B SaaS targets 3:1 or higher.
Freemium Model: Pricing strategy offering basic product functionality free while charging for advanced features or usage levels. Reduces acquisition friction and enables product-led growth. Requires careful feature gating.
Usage-Based Pricing: Charging based on actual product consumption rather than flat subscription fees. Common in infrastructure, API services, and AI features. Aligns costs with value but introduces revenue predictability challenges.
Price Anchoring: Cognitive bias where initial price exposure influences subsequent value perceptions. Competitors' pricing creates anchors that shape customer expectations. Must be considered when positioning pricing.
Tier Strategy: Designing multiple pricing levels with different feature sets and price points. Enables serving diverse customer segments while encouraging upgrades. Effective tiers show clear value differentiation.
Willingness-to-Pay (WTP): Maximum price customers will accept before rejecting purchase. Varies by segment and requires research to establish. Optimal pricing balances maximizing WTP capture while maintaining acceptable conversion.
References and Authoritative Sources
This analysis draws on research and insights from:
Industry leaders including Stripe, PayPal, Slack, Zoom, HubSpot, Microsoft, Notion, and Figma
All quantitative claims are drawn from published studies and verified market data from these authoritative sources.